티스토리 뷰
13장. 진짜로 만들기
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) |
모든 중복을 제거 하기 전까지는 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) 테스트를 완료 표시 할 수 없다. 코드는 중복코드는 없지만, 가짜 구현에 있는 아래 코드를 구현해 보자.
public Payment reduce(Expression source, String to) {
return Payment.card(0.25);
}
우선, 두 Payment 의 합은, RepresentPayment(대표지불수단) 이어야 한다.
@Test
public void testAddReturnsRepresentPayment() {
Payment card = Payment.card(0.25);
Expression representativePayment = card.add(card);
RepresentPayment representCard = (RepresentPayment) representativePayment;
assertEquals(card, representCard.representPayment);
assertEquals(card, representCard.addtionPayment);
}
연산의 외부 행위가 아닌 내부 구현에 너무 깊게 관여하고 있지만, 일단 테스트를 통과하기 위해 힘쓰자.
card.add() 는 RepresentPayment이 아닌 Payment를 반환하게 되어 있기 때문에, java.lang.ClassCastException 을 발생 시킨다.
package com.example.demo;
public class RepresentPayment implements Expression{
Payment representPayment;
Payment addtionPayment;
RepresentPayment(Payment representPayment, Payment addtionPayment) {
this.representPayment = representPayment;
this.addtionPayment = addtionPayment;
}
}
위와 같이 구현해 준 뒤, 테스트를 실행하면 성공!

아래 테스트는 reduce 가 임의로 구현되어 있기 때문에 실패하게 된다.
@Test
public void testRepresentPaymentAdd() {
Expression add = new RepresentPayment(Payment.card(0.2), Payment.card(0.2));
OnlineShoppingMall onlineShoppingMall = new OnlineShoppingMall();
Payment result = onlineShoppingMall.reduce(add, "Korea");
assertEquals(Payment.card(0.2), result);
}
reduce 를 구현 하면
package com.example.demo;
public class OnlineShoppingMall {
public Payment reduce(Expression source, String to) {
RepresentPayment representPayment = (RepresentPayment) source;
double chargeRate = (representPayment.representPayment.chargeRate + representPayment.addtionPayment.chargeRate) / 2;
return new Payment(chargeRate, to);
};
}
테스트는 성공 하지만 아래 이유로 코드가 너무 지저분 하다.
1. 캐스팅(형변환), 이 코드는 모든 Expression에 대해 작동해야 한다.
2. 공용(public) 필드와 그 필드들에 대한 두 단계에 걸친 레퍼런스.
이를 수정하도록 하자.
package com.example.demo;
public class RepresentPayment implements Expression{
Payment representPayment;
Payment addtionPayment;
RepresentPayment(Payment representPayment, Payment addtionPayment) {
this.representPayment = representPayment;
this.addtionPayment = addtionPayment;
}
public Payment reduce(String to) {
double chargeRate = (representPayment.chargeRate + addtionPayment.chargeRate) / 2;
return new Payment(chargeRate, to);
}
}
RepresentPayment.reduce의 인자로 Payment 를 넘겼을 경우를 테스트 항목에 추가 한다.
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) RepresentPayment.reduce(Payment) |
막대가 초록색이고, 위의 코드에 대해 더 할 것이 명확하지 않으니까 일단 그 테스트를 작성하도록 하자.
@Test
public void testReducePayment() {
OnlineShoppingMall onlineShoppingMall = new OnlineShoppingMall();
Payment result = onlineShoppingMall.reduce(Payment.card(0.2), "Korea");
assertEquals(Payment.card(0.2), result);
}public Payment reduce(Expression source, String to) {
if (source instanceof Payment) return (Payment) source;
RepresentPayment representPayment = (RepresentPayment) source;
return representPayment.reduce(to);
};
테스트는 통과 했으나, 코드가 너무 더럽다.
Expression 인터페이스에 reduce(String) 하면 아래와 같이 간결해 진다.
package com.example.demo;
public class OnlineShoppingMall {
public Payment reduce(Expression source, String to) {
return source.reduce(to);
};
}
다음장에서는 실제로 대표결제수단을 변경하는 기능을 구현해볼 것이다.
14장 바꾸기
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) Payment 에 대한 대표결제수단을 가져오는 Reduce |
대표결제수단을 card(0.2) -> account(0.3) 으로 바꾸는 테스트를 만들어 보자.
@Test
public void testReduceRepresentPaymentDiffChargeRate() {
OnlineShoppingMall onlineShoppingMall = new OnlineShoppingMall();
onlineShoppingMall.changeRepresentPayment(Payment.card(0.2), Payment.account(0.3));
Payment result = onlineShoppingMall.reduce(Payment.account(0.3), "Korea");
assertEquals(Payment.account(0.3), result);
// onlineShoppingMall 에서 정말 대표 결제수단이 변경 되었을까?
assertEquals(onlineShoppingMall.getChangeRepresentPayment(), result);
}
여기서 부터는 14장 책의 예제와 조금 다르다, 나는 onllineShoppingMall 에서 정말 대표 결제 수단이 변경되었는지 알고 싶기 때문에 아래 테스트 코드를 작성하고 함수를 개발 하였다.
그런데... 이 reduce 가 해줘야 하는 일이, 대표 결제 카드를 변경해 주는 역할을 해줘야 하는데, 해당 구현이 잘 못 되었다. Reduce 라는 이름도 이상하고... reduce -> changeRepresentPayment 로 이름을 변경하고 다시 테스트 해보겠다.
모든 테스트가 엄청난 빨간 막대를 만들며 난리가 났다... 이럴때 TDD 가 위력을 발휘 해야 겠지...? 테스트 코드는 두고 로직을 열심히 바꾸어야 겠다. 우선은 요구 사항 부터 수정하고 진행 하자.
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) RepresentPayment.changeRepresentPayment(Payment) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) OnlineShoppingMall 에 대한 대표결제수단을 가져오는 getRepresentPayment |
다시 초기로 돌아간 느낌이다 ㅎㅎ....
java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.example.demo.Payment.equals(Payment.java:18)
at org.junit.jupiter.api.AssertionUtils.objectsAreEqual(AssertionUtils.java:193)
at org.junit.jupiter.api.AssertEquals.assertEquals(AssertEquals.java:181)
at org.junit.jupiter.api.AssertEquals.assertEquals(AssertEquals.java:177)
at org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals(Assertions.java:1141)
at com.example.demo.CardTest.newAccountIssuanceTest(CardTest.java:19)
...
수정 중에 equals 에서 계속 에러가 났다. 확인해 보니
Payment newIssuance(double chargeRate) {
if (getClass().equals(Card.class)) {
return Payment.card(chargeRate);
} else if (getClass().equals(Account.class)){
return Payment.account(chargeRate);
} else {
return null;
}
}
getClass 할때에 Card, Account 로 오는게 아니라 호출한게 모두 Payment 로 온다. 해당 코드가 문제 이므로, 아래와 같이 수정한다.
가장 중요한건 테스트 코드 부터 수정해야 한다.
@Test
void newCardIssuanceTest() {
Payment newCard = Payment.card(0.2);
assertEquals(Payment.card(0.2), newCard.newIssuance(0.2, "card"));
assertEquals(Payment.card(0.3), newCard.newIssuance(0.3, "card"));
}
@Test
void newAccountIssuanceTest() {
Payment newAccount = Payment.account(0.2);
assertEquals(Payment.account(0.2), newAccount.newIssuance(0.2, "account"));
assertEquals(Payment.account(0.3), newAccount.newIssuance(0.3, "account"));
}
Payment newIssuance(double chargeRate, String type) {
if ("card".equals(type)) {
return Payment.card(chargeRate);
} else if ("account".equals(type)){
return Payment.account(chargeRate);
} else {
return null;
}
}
이렇게 하니 위의 테스트는 통과 했지만...
공포의 빨간 줄이 3개나 있다...

모두 테스트를 통화 하게 수정했다....
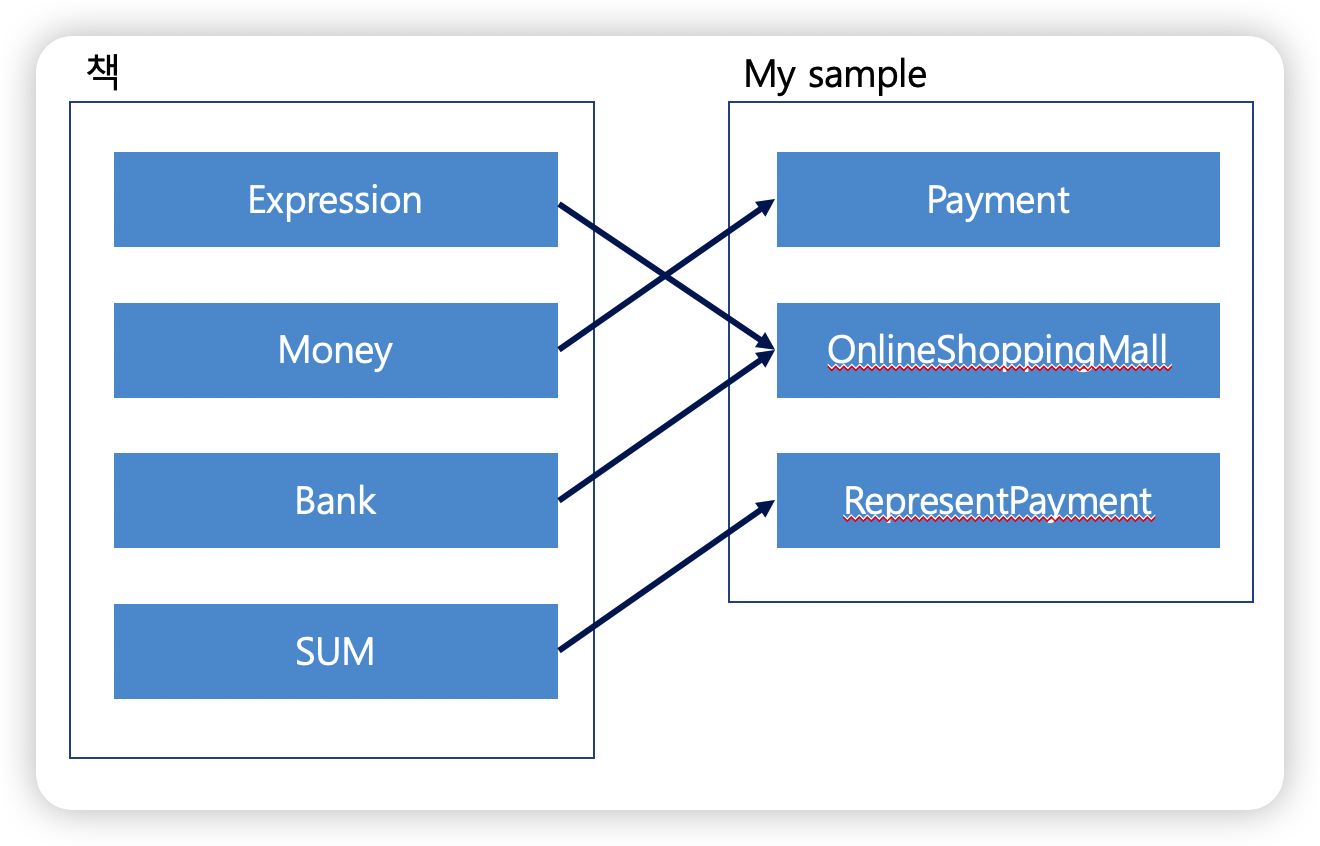
해당 코드를 바꾸면서, Expression 에 대한 쓸모가 해당 구조에는 안맞음이 느껴졌고, 테스트 코드가 있어서 사이드 이팩트 없이(?) 로직을 수정 하였다. 책에서는 궁극적으로 Excpression 에 로직을 넣는 모습인데, 나의 예제의 경우는 onLineShoppingMall 에 모든 로직이 들어갈 것으로 보인다.
결국 추상화로 코드가 간결해 지고 구조화가 되는 구조 인데, 나의 예제와는 좀 다른 점이 있기 때문에, 15,16,17 장에 내용은 아래 요구 사항에 맞게 진행 하는 것으로 하겠다.
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) RepresentPayment.changeRepresentPayment(Payment) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) OnlineShoppingMall 에 대한 대표결제수단을 가져오는 getRepresentPayment |
마지막. 결국은 요구사항에 맞게 내멋대로 진행
책에 스텝에 맞게 요구 사항을 만들었다고 생각했으나, 비지니스와 도메인이 다르다 보니 조금 차이가 있었다.
우선 요구 사항을 마무리 하고 리뷰 및 차이점을 정리해 보도록 하겠다.
| 카드 수수료(0.2) + 계좌 수수료(0.3) = 결제 금액 (복합결제가 가능 50대 50 으로만 결제 가능) 카드 수수료(0.2) + 카드 수수료(0.3) |
두가지 남은 요구 사항을 테스트 코드를 작성한다.
@Test
public void testCardAddAccount() {
OnlineShoppingMall onlineShoppingMall = new OnlineShoppingMall();
// 0.2 수수료 카드 추기
onlineShoppingMall.setPayment(Payment.card(0.2));
// 0.3 수수료 카드 결제수단 추가
onlineShoppingMall.getPayment().add(Payment.card(0.3));
assertTrue(onlineShoppingMall.getPayment().addPayment.equals(Payment.card(0.3)));
}
@Test
public void testPay() {
OnlineShoppingMall onlineShoppingMall = new OnlineShoppingMall();
// 0.2 수수료 카드 추기
onlineShoppingMall.setPayment(Payment.card(0.2));
// 0.3 계좌 결제수단 추가
onlineShoppingMall.getPayment().add(Payment.account(0.3));
// 결제 금액 가져 오기
assertEquals(onlineShoppingMall.getPayAmt(1000), 750);
}
완성 코드
package com.example.demo;
public class Account extends Payment{
Account(double chargeRate, String country, String type) {
super(chargeRate, country, type);
}
}
package com.example.demo;
public class Card extends Payment{
Card(double chargeRate, String country, String type) {
super(chargeRate, country, type);
}
}
package com.example.demo;
public class OnlineShoppingMall {
Payment representPayment = null;
Payment payment;
public boolean changeRepresentPayment(Expression source, Payment payment) {
return source.changeRepresentPayment(payment);
};
public Payment getChangeRepresentPayment() {
return this.representPayment;
};
public boolean setChangeRepresentPayment(Payment payment) {
this.representPayment = payment;
return this.representPayment != null;
};
public boolean setPayment(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
return this.payment != null;
}
public Payment getPayment() {
return this.payment;
}
public double getPayAmt(int amt) {
double representPaymentChargeRate = this.payment.chargeRate + this.payment.addPayment.chargeRate;
return amt * (1 - (representPaymentChargeRate / 2));
}
}
package com.example.demo;
class Payment implements Expression{
protected double chargeRate = 0;
protected int chargeAmt = 0;
protected String country = "";
protected Payment representPayment = null;
protected Payment addPayment = null;
protected String type = "";
Payment(double chargeRate, String country, String type) {
this.chargeRate = chargeRate;
this.country = country;
this.type = type;
}
public boolean equals(Object object) {
Payment payment = (Payment) object;
if (this.chargeAmt != payment.chargeAmt) {
return false;
}
if (this.chargeRate != payment.chargeRate) {
return false;
}
if (this.type != payment.type) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
static Payment card(double chargeRate) {
return new Payment(chargeRate, "Korea", "card");
}
static Payment account(double chargeRate) {
return new Payment(chargeRate, "USA", "account");
}
Payment newIssuance(double chargeRate, String type) {
if ("card".equals(type)) {
return Payment.card(chargeRate);
} else if ("account".equals(type)){
return Payment.account(chargeRate);
} else {
return null;
}
}
public String country() {
return this.country;
}
public boolean add(Payment addPayment) {
this.addPayment = addPayment;
return this.addPayment != null;
}
public boolean changeRepresentPayment(Payment payment) {
this.representPayment = payment;
return this.representPayment != null;
}
}
package com.example.demo;
public class RepresentPayment implements Expression{
Payment representPayment;
Payment addtionPayment;
RepresentPayment(Payment representPayment, Payment addtionPayment) {
this.representPayment = representPayment;
this.addtionPayment = addtionPayment;
}
public boolean changeRepresentPayment(Payment payment) {
this.representPayment = payment.representPayment;
return this.representPayment != null;
}
}
테스트 all pass~
마지막으로 느낀점 및 구조 비교
구조 비교
느낀점
TDD 를 통해서 작은 기능을 구현하면서 테스트를 우선 구현하고 점진적으로 구조를 변경해 나가는 방법에 대해서 습득 했다. 하지만 실무에서 이렇게 점진적으로 구조화를 진행하면 너무 많은 단계와 리팩토링이 필요 할 듯 하다. 실무적으로 사용하기 위해서는 전체 요구사항을 명학화게 정의 하고, 테스트코드로 우선 작성을 하고, 구조화 같은 경우는 사전에 정의하고 진행 하는 것이 오히려 더 리소스가 적게들 것으로 생각이 된다. TDD 를 하면서 가장 좋았단건 역시, 로직 변경에대해서 사이드 이펙트가 적다는 점이지만, 테스트의 커버리지가 잘 되어 테스트가 의미가 있는지 잘생각해 봐야 할 것이며, 또한 요구사항 변경에 대해서 테스트를 유연하게 변경하는 작업도 필요 할듯 하다. 결론 적으로는 테스트의 범위, 요구사항을 정확한 파악, 테스트와 코드 리팩토링에 중심점을 잘 잡아야 TDD 로 개발 하는 방법이 실무적으로 잘 사용 될 것으로 생각이 된다.
참고 : 테스트 주도 개발 (켄트백)
'테스트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 테스트 주도 개발 - TDD 마스터 하기 (0) | 2023.03.19 |
|---|---|
| 테스트 주도 개발_5 (0) | 2023.02.12 |
| 테스트 주도 개발_4 (0) | 2023.02.12 |
| 테스트 주도개발_3 (0) | 2023.02.12 |
| 테스트 주도개발_2 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- mongodb
- TDD
- fastapi
- 켄트 백
- 웹서비스
- AWS
- 분산처리
- GateWayApi
- Python
- 테스트주도개발
- Python #FastAPI
- nodejs
- SpringBoot
- 웹개발
- kafka
- MQ
- 테스트
- MSA
- data crawling
- EC2
- 퀜트백
- 테스트 주도 개발
- data mining
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
